Diabetes is a major public health problem that is approaching epidemic proportions globally. Uncontrolled diabetes significantly impacts the patients’ quality of life: it may lead to loss of workdays, multiple hospital visits, reduced mobility, and even death. If a patient has diabetes, he/ she may also have obesity, dyslipidemia and hypertension. Each of these conditions is linked to a number of serious problems, including diabetes related complications like heart disease, loss of vision, kidney failure, nerve damage, and even amputation.
The Indian healthcare sector is growing at a rapid pace due to increased investment by public as well as private players. Together the pharmaceuticals industry and the healthcare delivery industry, which includes hospitals, nursing homes and diagnostics centres constitutes 65 percent of the overall healthcare market. There is significant scope for enhancing healthcare services considering that healthcare spending as a percentage of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is rising year on year. AS per World Health Organization, in India 70 million people live with diabetes and an additional 36 million remain ignorant of their condition. This means that nearly 1 in 10 Indians suffers from this condition but is either unaware of it or is slipping through the treatment cracks with inadequate reporting and monitoring.
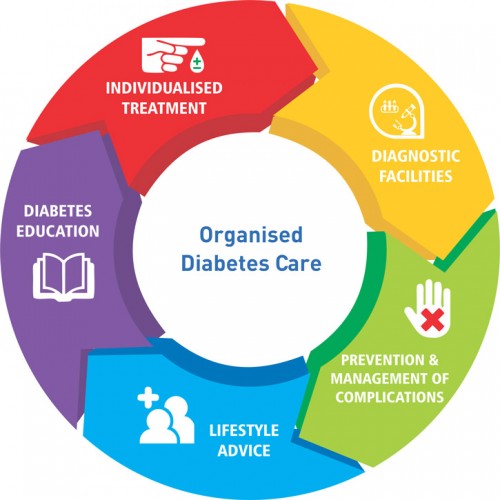
Such gaps in chronic disease management provide an opportunity for technology driven clinical organizations to intelligently use technology which can make a huge difference in the management of diabetes. Such clinical organizations have the potential to bring about a paradigm shift in diabetes management system in India by moving it from a deeply fragmented model to a 360-degree comprehensive care model.
A productive and informative interaction between the patient, physician and the care team by using information technology based interventions can lead to improved diabetes care. Existing and emerging technologies such as wireless devices, smart glucometers, Bluetooth devices, and the internet can help facilitate patient self-management of diabetes. Such devices provide a practical and cost-effective method for monitoring clinical outcomes and increasing patient adherence to treatments.